The most important question of Rectifiers and Filters in Electronic Devices and Circuits; explain the operation of the Half-wave Rectifier and represent the input and output wave forms? is being answered here.
Half-Wave Rectifier:
A Half – wave rectifier is one which converts a.c. voltage into a pulsating voltage using only one half cycle of the applied a.c. voltage.
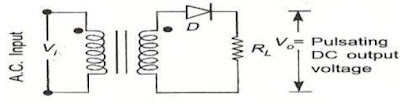 |
| Fig. a Basic structure of Half-Wave Rectifier |
The half-wave rectifier circuit shown in above figure consists of a resistive load, a rectifying element i.e., p-n junction diode and the source of a.c. voltage, all connected is series. The a.c. voltage is applied to the rectifier circuit using step-down transformer.
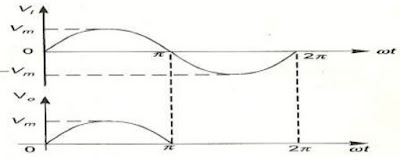 |
| Fig.b Input and output waveforms of a Half wave rectifier |
The input to the rectifier circuit, V=Vm sinwt, where Vm is the peak value of secondary a.c. voltage.
Operation: For the positive half-cycle of input a.c. voltage, the diode D is forward biased and hence it conducts. Now a current flows in the circuit and there is a voltage drop across RL. The waveform of the diode current (or) load current is shown in figure.For the negative half-cycle of input, the diode D is reverse biased and hence it does not conduct. Now no current flows in the circuit i.e., i=0 and Vo=0. Thus for the negative halfcycle no power is delivered to the load.


Where is this option full wave diode rectifier
ReplyDelete