The most important question of Rectifiers and Filters in Electronic Devices and Circuits; explain Rectifier Characteristics and diode designs? is being answered here.
RECTIFIER:
Any electrical device which offers a low resistance to the current in one direction but a high resistance to the current in the opposite direction is called rectifier. Such a device is capable of converting a sinusoidal input waveform, whose average value is zero, into a unidirectional waveform, with a non-zero average component.
A rectifier is a device which converts a.c. voltage (bi-directional) to pulsating d.c. voltage (Uni-directional).
Characteristics of a Rectifier Circuit:
1. Load currents: They are two types of output current. They are average or d.c. current and RMS currents.
i) Average or DC current: The average current of a periodic function is defined as the area of one cycle of the curve divided by the base. It is expressed mathematically as
ii) Effective (or) R.M.S. current: The effective (or) R.M.S. current squared of a periodic function of time is given by the area of one cycle of the curve which represents the square of the function divided by the base. It is expressed mathematically as
2. Load Voltages: There are two types of output voltages. They are average or D.C. voltage and R.M.S. voltage.
i) Average or DC Voltage: The average voltage of a periodic function is defined as the areas of one cycle of the curve divided by the base. It is expressed mathematically as
ii) Effective (or) R.M.S Voltage: The effective (or) R.M.S voltage squared of a periodic function of time is given by the area of one cycle of the curve which represents the square of the function divided by the base.
3. Ripple Factor: It is defined as ration of R.M.S. value of a.c. component to the d.c. component in the output is known as “Ripple Factor”.
4. Efficiency: It is the ratio of d.c output power to the a.c. input power. It signifies, how efficiently the rectifier circuit converts a.c. power into d.c. power. It is given by
5. Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV):It is defined as the maximum reverse voltage that a diode can withstand without destroying the junction.
6. Regulation: The variation of the d.c. output voltage as a function of d.c. load current is called regulation. The percentage regulation is defined as
For an ideal power supply, % Regulation is zero.
Using one or more diodes in the circuit, following rectifier circuits can be designed.
1. Half - Wave Rectifier
2. Full – Wave Rectifier
3. Bridge Rectifier


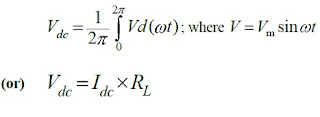




No comments:
Post a Comment
Dear visitor, kindly ask us whatever you want related to Electronic Devices and Circuits through comment(s). They will be posted as soon as possible which will be helpful to your development and our improvement. Encourage us by asking and staying connected with us always, thank you. Interested to work for this site (blog), whatsapp @ 7893356131 - NRR.